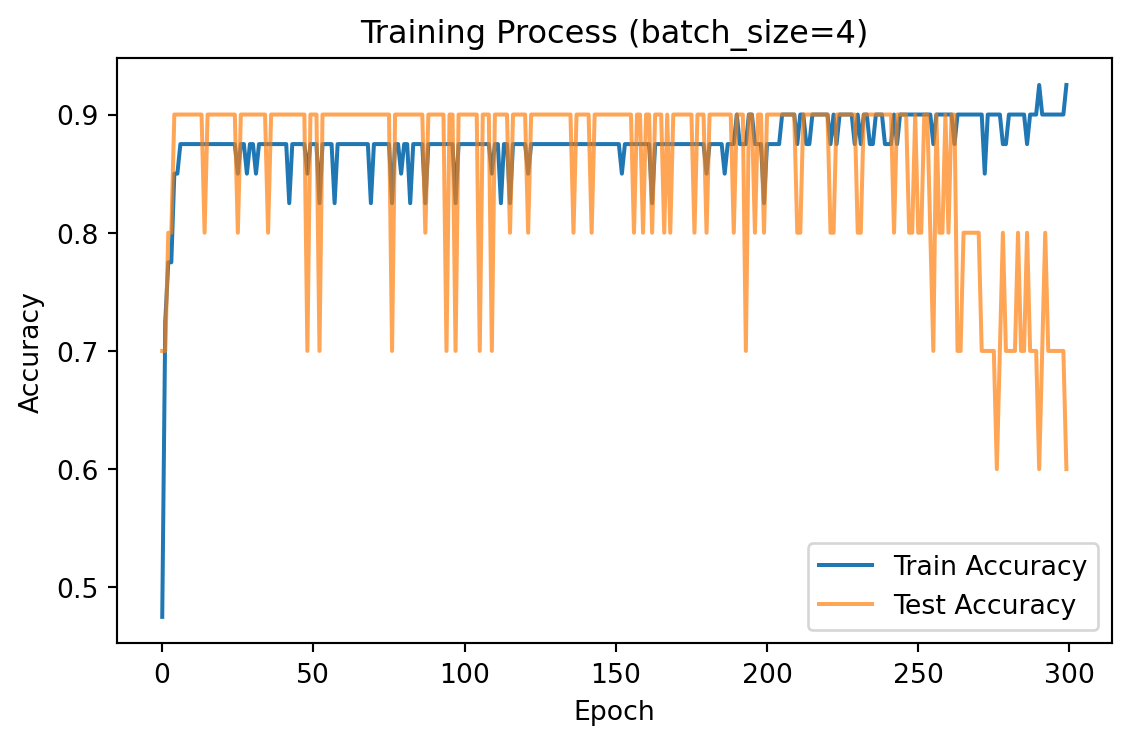
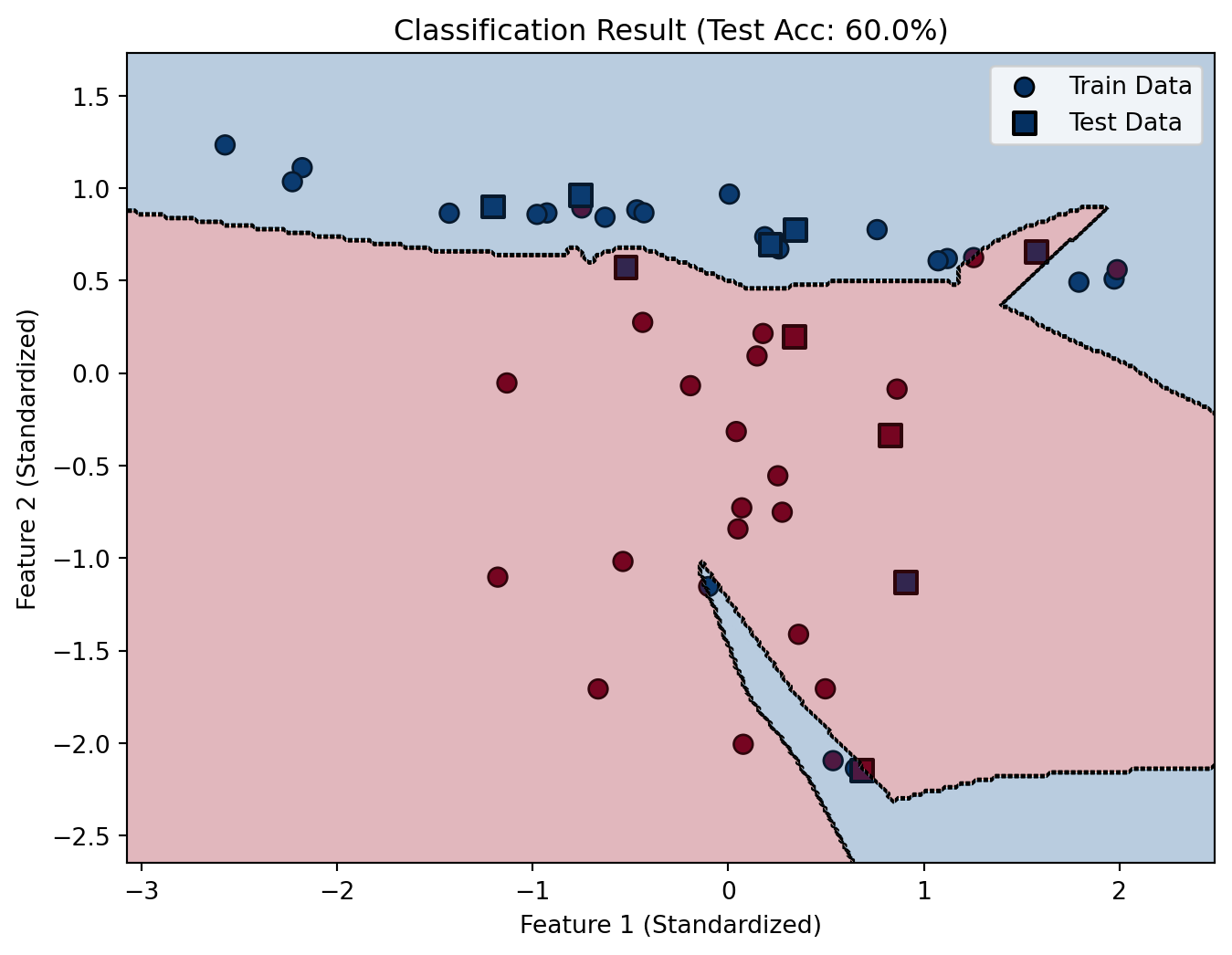
# 在之前的代码训练结束后添加以下内容
# 生成网格点以绘制决策边界
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y):
# 设置网格范围和步长
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 0.5, X[:, 0].max() + 0.5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 0.5, X[:, 1].max() + 0.5
h = 0.02 # 步长
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# 将网格点转换为PyTorch张量
grid_tensor = torch.tensor(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()], dtype=torch.float32)
# 模型预测
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
Z = model(grid_tensor)
Z = torch.argmax(Z, dim=1).numpy()
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# 绘制填充轮廓
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.3, cmap='RdBu')
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, colors='black', linewidths=0.5, linestyles='dashed')
# 创建新的可视化结果图
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
# 绘制训练集和测试集数据点
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap='RdBu',
edgecolors='k', label='Train Data', s=60)
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap='RdBu',
edgecolors='k', marker='s', linewidth=1.5, label='Test Data', s=80)
# 绘制决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(model, X_tensor.numpy(), y_tensor.numpy())
# 添加图例和标签
plt.title(f"Classification Result (Test Acc: {test_acc_history[-1]:.1%})")
plt.xlabel("Feature 1 (Standardized)")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2 (Standardized)")
plt.legend()
plt.show()